104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
🟩 Easy
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1
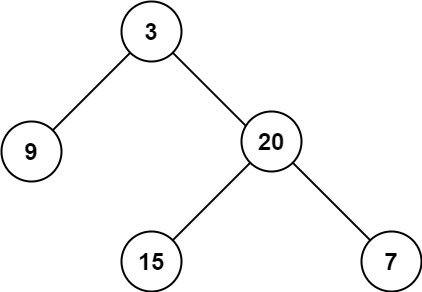
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 3
Example 2
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: 2
Constraints
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 10^4].-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solution
My Solution
Optimal Solution (Concise DFS)
Alternative Solution (Iterative BFS)
Approach Analysis
This problem can be solved in multiple ways:
Your Solution (Explicit DFS):
Handles each case separately
Very clear and readable
Explicitly checks for leaf and single-child cases
Good for understanding the problem
Optimal DFS Solution:
More concise implementation
Implicitly handles all cases
Same time/space complexity
Relies on max function elegantly
BFS Alternative:
Level-order traversal
Counts depth level by level
Uses queue data structure
Good for level-based operations
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
All solutions visit each node exactly once
Constant work per node
n is total number of nodes
Space Complexity
DFS Solutions: O(h)
h is height of tree
Recursive call stack
Best: O(log n) for balanced
Worst: O(n) for skewed
BFS Solution: O(w)
w is maximum width of tree
Queue size at widest level
Best: O(1) for skewed
Worst: O(n/2) for perfect binary tree
Why Different Approaches Work
Your Solution:
Explicit case handling
Clear logic flow
Good for debugging
Easy to modify for variations
Optimal DFS:
Mathematical elegance
Recursive subproblem
Minimal code
Same efficiency
BFS Approach:
Natural level counting
No recursion needed
Easy to modify for related problems
Good for level-specific tasks
Common Patterns & Applications
Similar Problems:
Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Balanced Binary Tree
Diameter of Binary Tree
Tree Traversal Patterns:
DFS: Pre/In/Post order
BFS: Level order
Each has its use cases
When to Use Each:
DFS: Path-related problems
BFS: Level-related problems
Your solution: When clarity is priority
Optimal: When conciseness matters

Leetcode: link
Last updated