54. Spiral Matrix
🟧 Medium
Given an m x n matrix, return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.
Example 1
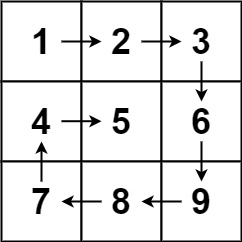
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
Example 2
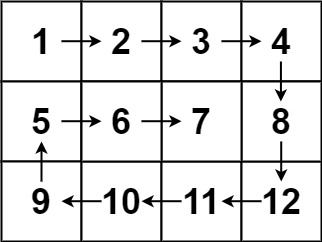
Input: matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]] Output: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
Constraints
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10-100 <= matrix[i][j] <= 100
Hint 1
Well for some problems, the best way really is to come up with some algorithms for simulation. Basically, you need to simulate what the problem asks us to do.
Hint 2
We go boundary by boundary and move inwards. That is the essential operation. First row, last column, last row, first column, and then we move inwards by 1 and repeat. That's all. That is all the simulation that we need.
Hint 3
Think about when you want to switch the progress on one of the indexes. If you progress on i out of [i, j], you'll shift in the same column. Similarly, by changing values for j, you'd be shifting in the same row. Also, keep track of the end of a boundary so that you can move inwards and then keep repeating. It's always best to simulate edge cases like a single column or a single row to see if anything breaks or not.
Solution
My Solution
Optimal solution

Leetcode: link
Last updated