206. Reverse Linked List
Example 1
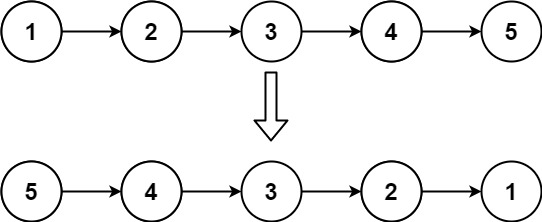
Example 2
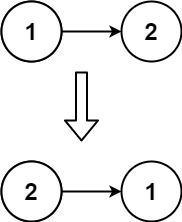
Example 3
Constraints
Solution
Approach Analysis
Visualization of Both Approaches
Iterative Process
Recursive Process
Complexity Analysis
Iterative Solution
Recursive Solution
Why Both Solutions Work
When to Use Each
Common Patterns & Applications
Interview Tips

Last updated