11. Container With Most Water
🟧 Medium
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the i^th line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1
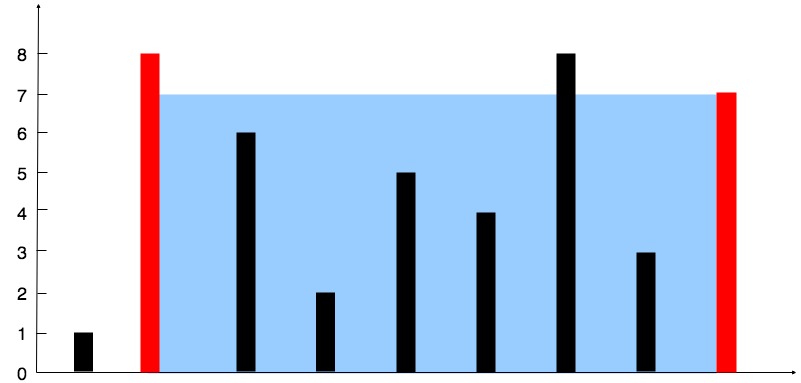
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] Output: 49 Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2
Input: height = [1,1] Output: 1
Constraints
n == height.length2 <= n <= 10^50 <= height[i] <= 10^4
Solution
My Solution
Optimal Solution (Two Pointer Approach)
Approach
The Two Pointer technique is used to solve this problem efficiently:
Initialize two pointers:
Left pointer at the start (index 0)
Right pointer at the end (index n-1)
Calculate area at each step:
Width = right - left (distance between lines)
Height = min(height[left], height[right])
Current area = width * height
Update maximum area if current area is larger
Move pointers strategically:
If height[left] < height[right], move left pointer right
If height[right] <= height[left], move right pointer left
This ensures we always explore the possibility of finding a larger area
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(n)
We traverse the array exactly once
Each element is visited at most once by either left or right pointer
All operations inside the loop (min, max) are O(1)
Space Complexity: O(1)
We only use three variables regardless of input size:
maxArea - to store the maximum area
left - left pointer
right - right pointer
Why it works
Uses two pointers to track potential container boundaries
Always moves the pointer with smaller height inward
Area is limited by the smaller height, so moving the taller pointer would never give a better result
Efficiently finds the maximum area by considering all possible optimal container configurations

Leetcode: link
Last updated